UP Development - 3.Construction
Design Phase
- the design phase focuses on questions of how – how the system fulfills the requirements
- the design phase emphasizes a logical solution from the perspective of objects ( and interfaces )
- the heart of the solution is the creation of the following two diagrams, which are part of the Design Model in UP.
- Interaction Diagrams
- How objects communicate, dynamic aspects
- Class Diagram
- static object relationships, static aspect
- Interaction Diagrams
( 구조적 측면의 Solution - Class Diagram )
( 행동적 측면의 Solution - Interaction Diagram )
Interaction Diagram
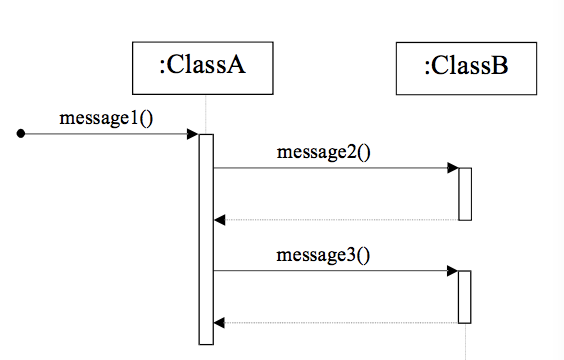
Sequence Diagram
- Focuses on the Time
- order in which the messages are sent
- 참여 객체가 많아지면 표현 공간이 많이 필요
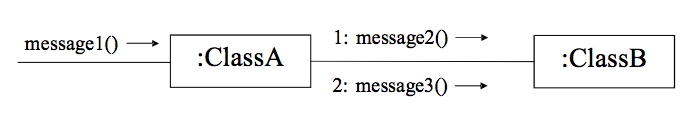
Communication Diagram
- Focuses on the Space
- relationships between objects
- sequence diagram 과 보여주는 것은 같지만
표현 공간을 절약시켜준다.
-> 시간의 축이 없기때문에 메시지에 번호를 부여하여
순서를 판단한다. - 표현 공간이 덜 필요
UML Object Icons
![]()
1.Communication Diagram
Illustrating Messages
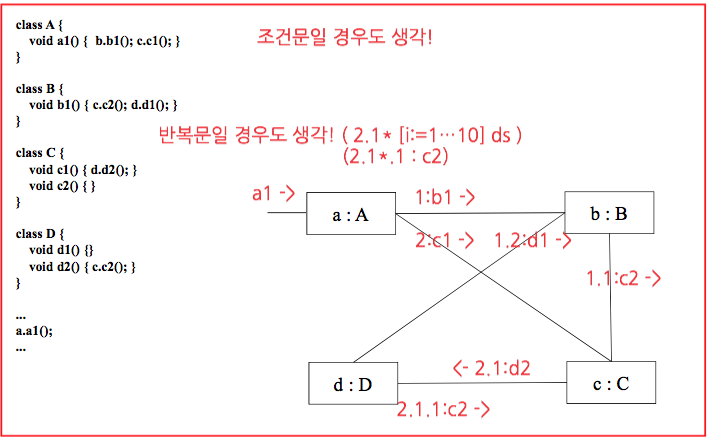
메세지간의 인과관계를 부여하기 위해 k 번 메세지의 응답을 k.1 , k.2 … 로 표현한다.
- Self Message
자기 자신에게 보내는 message 표기법
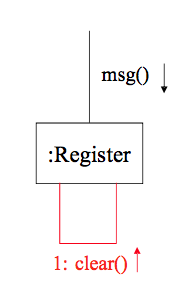
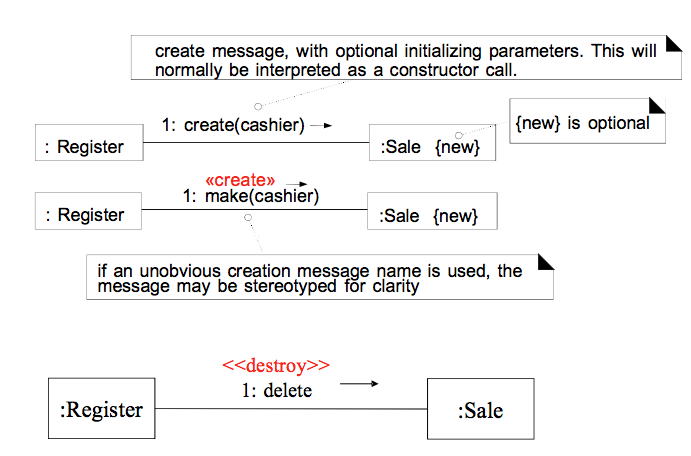
- Object Creation & Deletion
객체 생성 및 제거 표기법
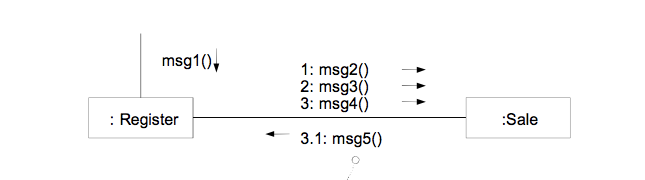
- Return Value
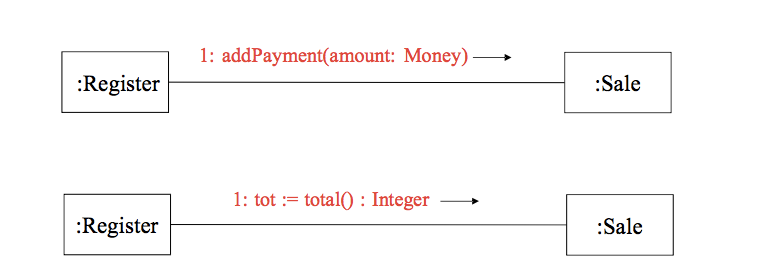
–> 리턴값의 타입은 Integer 이며 total() 함수의 리턴 값으로 tot 를 받는다.
Message Number Sequencing
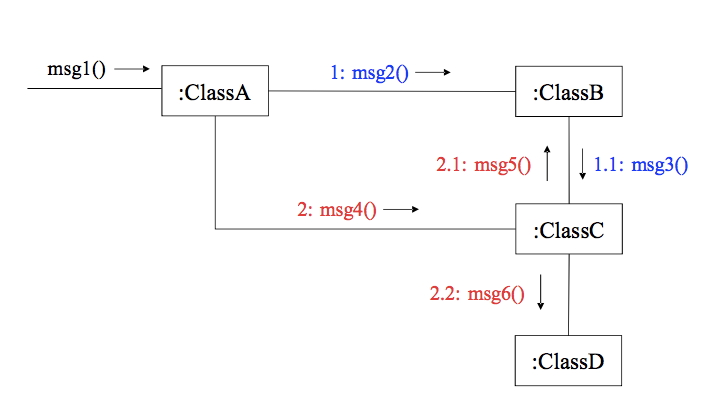
( Unconditional Message )
메세지간의 인과관계를 부여하기 위해 k 번 메세지의 응답을 k.1 , k.2 … 로 표현한다.
msg1 : trigger message (최초 메세지) 1 / 1.1 msg 가 끝나면 2: msg4() 가 동작 —> :classD 에서 메소드를 하나 더 생성한다면 2.2 msg 로 부터 classD 가 생성되었기 때문에 2.2.1 부터 부여한다.
Sudo Code
class ClassA {
msg1() {
b.msg2();
c.msg4();
}
}
class ClassB {
msg2() {
c.msg3();
}
…
}
class ClassC {
msg4() {
b.msg5();
d.msg6();
}
}
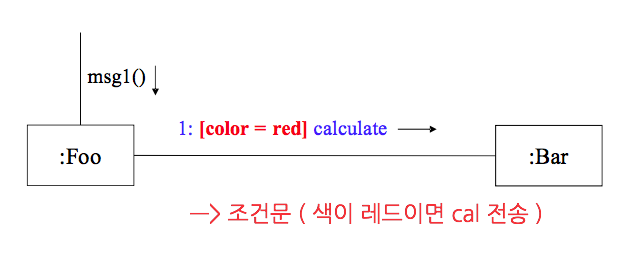
…- Conditional Messages
- Iteration or Looping
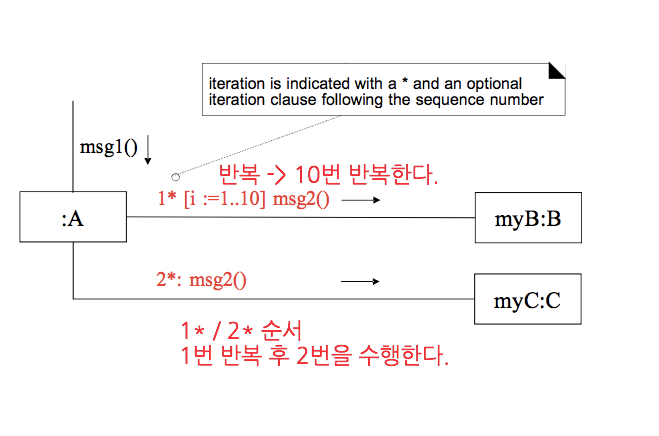
1.
for () {
msg1()
msg2()
}
2.
for () {
msg1()
}
for () {
msg2()
}
—> 구분하는 방법 ( 미리 약속을 정해서 구분해야 한다)
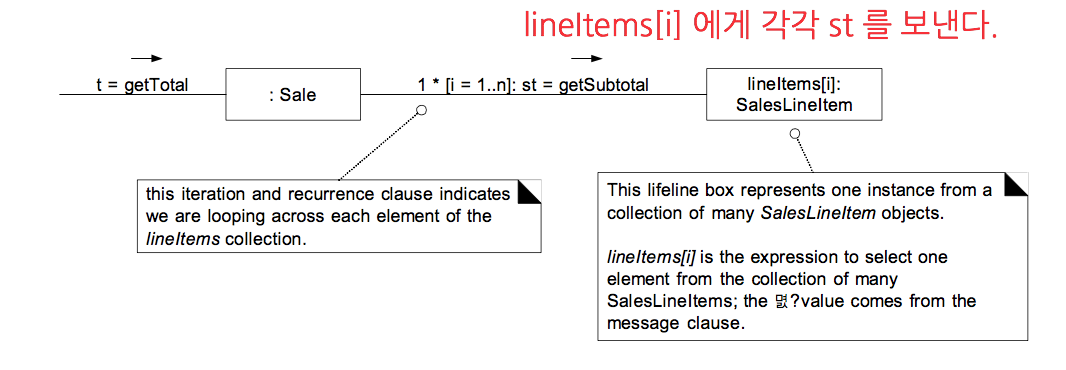
—> Communication Diagram 의 취약점- Illustrating Iterations
- Active Objects & Asynchronous Messages
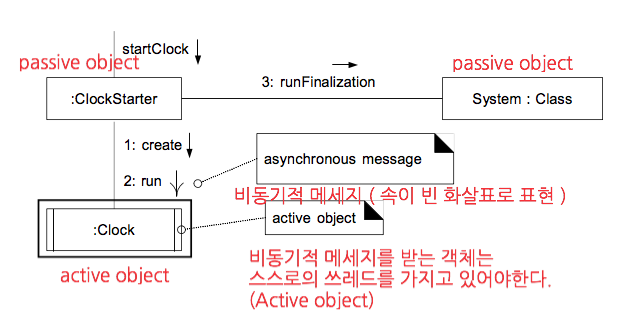
Example