Unranked Retrieval Evaluation
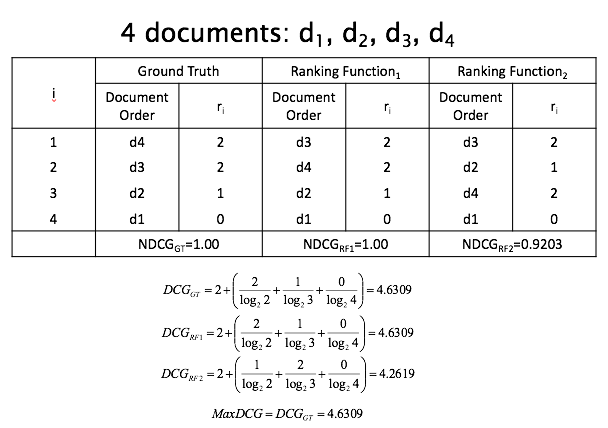
Discounted Cumulative Gain
-
Popular measure for evaluating web search and related tasks
- Two Assumptions
-
Highly relevant documents are more useful than marginally relevant documents
-
the lower the ranked position of a relevant document, the less useful it is for the user, since it is less likely to be examined
-
-
Gain is accumulated starting at the top of the ranking and may be reduced, or discounted, at lower ranks
- Typical discount is 1/log (rank)
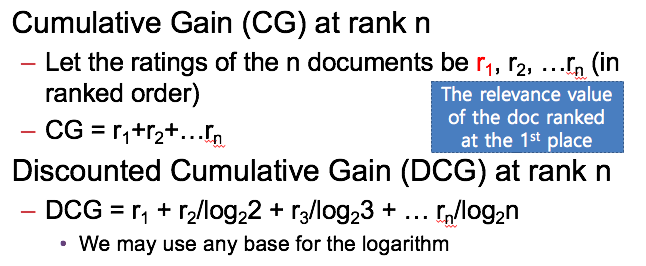
Cumulative Gain (CG) at rank n
n => # of docs
r1, r2, …rn = score of benchmarking docs ( search engine 이 찾은 순서 )
Discounted Cumulative Gain (DCG) = > 높은 rank 에게 작은 log 값을 부여한다.
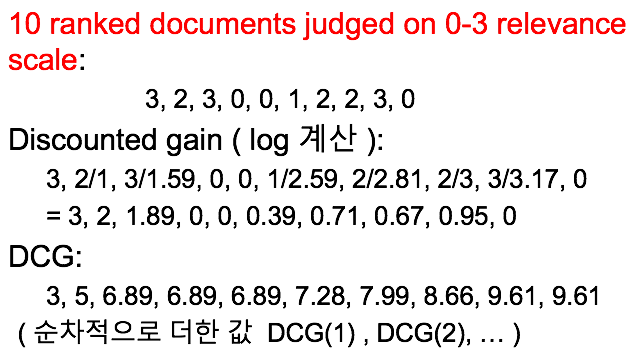
Ex) D1 , 3 / D2 , 4 / D3 , 5 -> sequence case r1 = 3 r2 = 4 r3 = 5 CG = r1 + r2 + r3 = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 DCG = r1 + r2/log2 + r3/log3 = 3 + 4 + 5/log3 = 7 + 5/log3 Optimal case r1 =5 r2 = 4 r3 =3 CG = r1 + r2 + r3 = 5 + 4 + 3 = 12 DCG = r1 + r2/log2 + r3/log3 = 5 + 4/log2 + 3/log3 = 9 + 3/log3
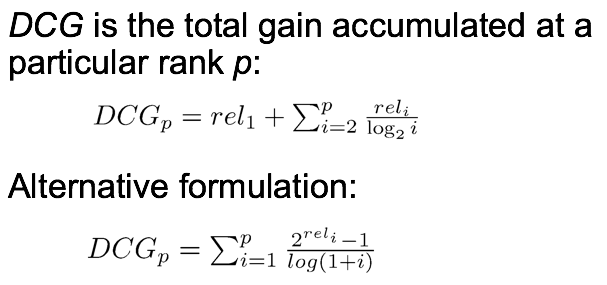
Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain
-
Normalize DCG at rank n by the DCG value at rank n of the ideal ranking
-
The ideal ranking would first return the documents with the highest relevance level, then the next highest relevance level