Model
- A Model is a simplification of Reality
- Models capture the Essential aspects of a system which are relevant to a given level of Abstraction ( 모델 : 필수적 요소만 나타낸것 )
Reasons of using Model
- To Visualize a system as it’s or as we want it to be
- To Specify the structure or behavior of a system
- To give a blueprint to Construct a system
- To Document the decisions we have made
A Model may be structural or behavioral
- Static Models ( Structure Models )
Describe a structural prperties of a system
- Dynamic Models ( Behavior Models )
Describe a behavioral properties of a system
Unified Modeling Language (UML 2.0)
- Visual Notation ans semantics
- Process Independent
- Not Process, Just Notation
- Static Models ( Structure Models )
- Class Diagrams
- Object Diagrams
- Component Diagrams
- Deployment Diagrams
- Package Diagrams
- Composite Structure Diagrams
- Dynamic Models ( Behavior Models )
- Activity Diagrams
- Use Case Diagrams
- State Machine Diagrams
- Interaction Diagrams
1. Sequence Diagram
2. Communication Diagram
3. Interaction Overview Diagrams
4. Timing Diagrams
Ways of Using UML
- Different ways in which people want to use UML
- UML as sketch
- UML as blueprint
- UML as programming language
실질 적으로 대부분 sketch 까지만 진행
- Forward Engineering
- draws a UML diagram before you write code
- Reverse Engineering
- builds a UML diagram from existing code in order to help understand it
Unified Process
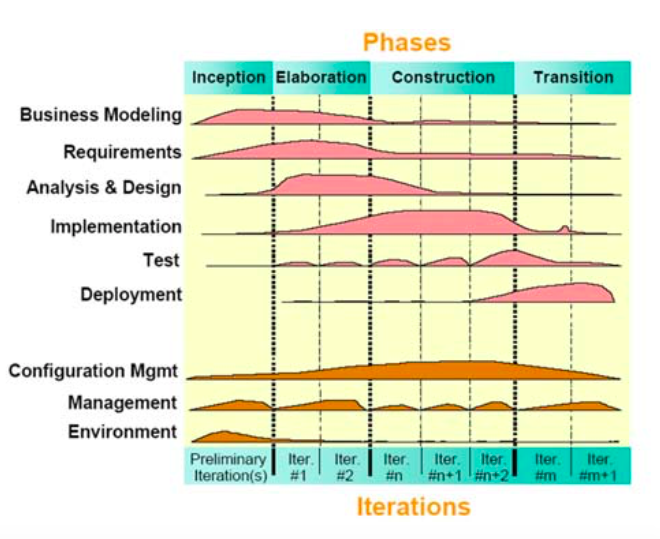
Inception -> Elaboration -> construction -> Transition
각각의 단계에서 달성해야 할 Goal 이 무엇인지 파악하는것이 매우 중요하다.
Object-Oriented Analysis
Analysis emphasizes an Investigation, Understanding, and Discovery of the problem domain and requirements what the problem is about and what a system must do
Analysis dosen’t concern how a logical solution is defined
All the vocalbularies used in the analysis must from the Problem Domain
- Requirement Analysis
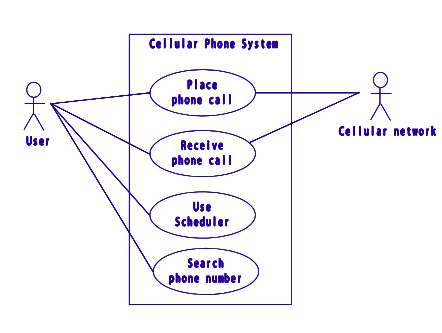
Investigation of functional & non - functional requirements Functional requirement are captured by Use-Case Model
- Object Analysis

Investigation of domain objects, i.e., emphasizing on finding and describing objects (or concepts) in the problem domain Captured by Domain Model
Object-Oriented Design
- OOD is primarily a process of Invention and Adaption of conceptual solution
- OOD tends to be relatively independent of the language used
Object-Oriented Programming
- This corresponds to the implementation discipline
- The classes and class operations are coded, tested, and intergrated
—> There is no one correct representation
Core of the Unified Process (UP)
Iterative and Incremental development process using a set of principles and methods based on Objects in the Problem Domain rather than actions performed by the system
-
Iterative
Instead of building the entire system as one go, the project has a few or many builds. A build includes only a subset of the entire functionality -
Incremental
Software is developed on top of previous build. Make small but noticeable improvements in each iteration
Additional UP Best Practices
- Tackle high-risk and high-value issues in early iterations ( 어려운 것을 먼저 한다 )
- Continuously engage users for evaluation, feedback and requirements ( 고객의 요구사항을 지속적으로 수용한다 )
- Build a cohesive, core Architiecture in early iterations ( 초반에는 응집적이며 중심구조적인 아키텍쳐로 설계한다 )
- Continuously verify quality; test early, often, and realistically ( 지속적인 테스트를 한다 )
- Apply Use Cases ( UP 중심에는 Use-Case 가 있다 )
- Model software visually ( with UML )
- Carefully manage requirements
- Practice change request and configuration management
UP Development Cycle
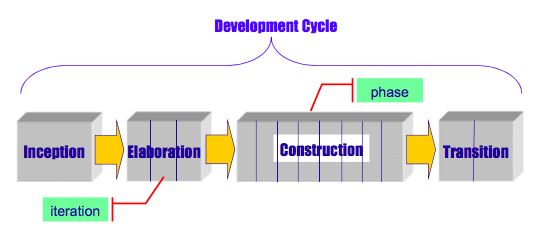
1. Inception
- Feasibility Phase ( 실현 가능한가? )
- Establish approximate vision and business case
2. Elaboration -> 시스템의 성패를 가르는 가장 중요한 단계
- Implement core architecture (시스템의 전체적인 모습이 완성되는 단계이다. )
- 수행 전 고객의 Requirement 의 80 ~ 90% 이상을 알고 있어야한다.
- Resovle High Risks ( 리스크 요소가 큰 것부터 해결한다 -> Elaboration 이 끝날때는 High Risk 가 없는게 지향적이다 )
3. Construction
- Iterative implementation of the remaining lower risk and easier elements
- Preparation for deployment
4. Transition
- Get User Feedback
UP Disciplines and Artifacts
- A discipline (관련분야) is a set of activities (and related artifacts) in one subject area, such as activities in requirements analysis
- An artifact (discipline 으로 만들어진 결과 산출물) is the general term used for any work product
Two Desert Island SKills in OOA & OOD
- Assigning responsibilities to software components
- Finding suitable objects or abstraction